If you’re a small business owner or startup trying to reach more customers online, you’ve probably heard of Google Ads.
It’s one of the most powerful advertising platforms out there—but if you’re new to it, it can feel a bit overwhelming. Don’t worry, though. In this Google Ads beginner guide for small businesses, we’ll walk you through the basics and give you a clear path to getting started.
Whether you’re launching your first ad or just exploring your options, this guide is designed to give you confidence and help you avoid common mistakes. Let’s dive in.
What Is Google Ads?
Google Ads (formerly known as Google AdWords) is Google’s online advertising platform.
It allows you to show your business ads to people who are actively searching for products or services like yours. These ads appear on Google search results, YouTube, Google Maps, and across a vast network of partner websites.
With Google Ads, you can:
- Target specific keywords and search terms
- Set a budget that works for you
- Drive traffic to your website
- Generate leads and sales
In short, it’s a flexible and scalable tool to grow your business online.
Why Should Small Businesses Use Google Ads?
When used correctly, Google Ads can help level the playing field for small businesses competing with larger brands. Here’s why it’s worth considering:
- Targeted Advertising:
You choose exactly who sees your ads based on location, keywords, device type, and even time of day. - Cost Control:
You only pay when someone clicks on your ad. Plus, you can set daily and monthly limits to stay on budget. - Measurable Results:
Google Ads provides detailed reporting so you can track what’s working and what’s not—and adjust accordingly. - Immediate Visibility:
SEO takes time. Google Ads can get your business to the top of search results almost instantly.
Key Terms You Should Know
Before we dive into setting things up, here are a few terms you’ll see often in Google Ads:
- CPC (Cost Per Click) – What you pay each time someone clicks on your ad.
- CTR (Click-Through Rate) – The percentage of people who click on your ad after seeing it.
- Keywords – The search terms people type into Google that can trigger your ad.
- Quality Score – Google’s rating of the relevance of your keywords, ads, and landing pages.
- Conversion – A desired action taken by a user, like making a purchase or filling out a contact form.
Step-by-Step: Setting Up Your First Google Ads Campaign
Now that you know the basics, let’s get your first campaign off the ground.
1. Create a Google Ads Account
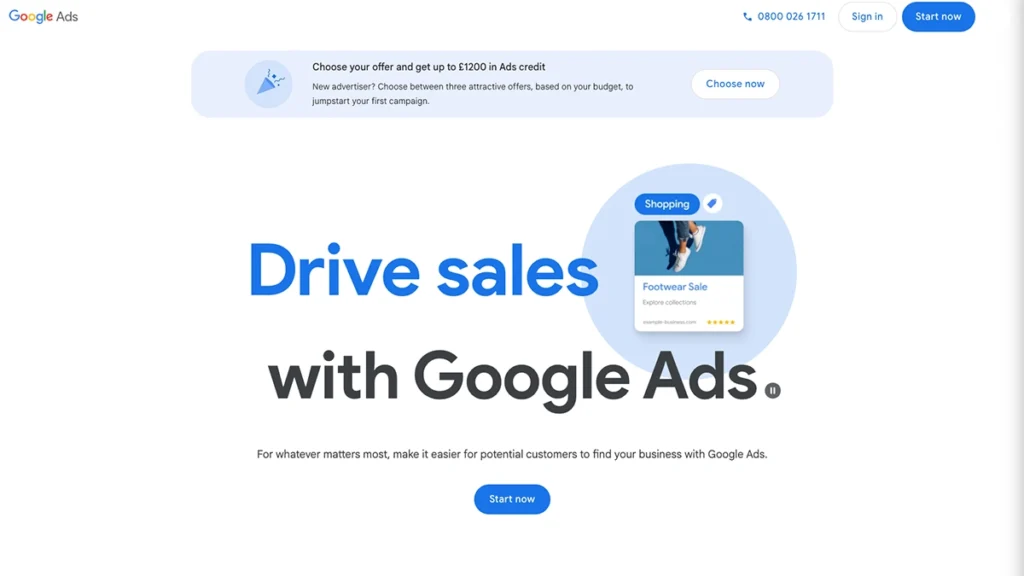
Go to ads.google.com and click Start Now. You’ll need a Google account to get going.
Follow the prompts to set up your business name, billing country, time zone, and currency. Once that’s done, you’ll land in your Google Ads dashboard.
2. Create a New Campaign
In your dashboard, click the + New Campaign button. You’ll be asked to choose a goal for your campaign — this is where things begin to take shape.
Choose Your Objective
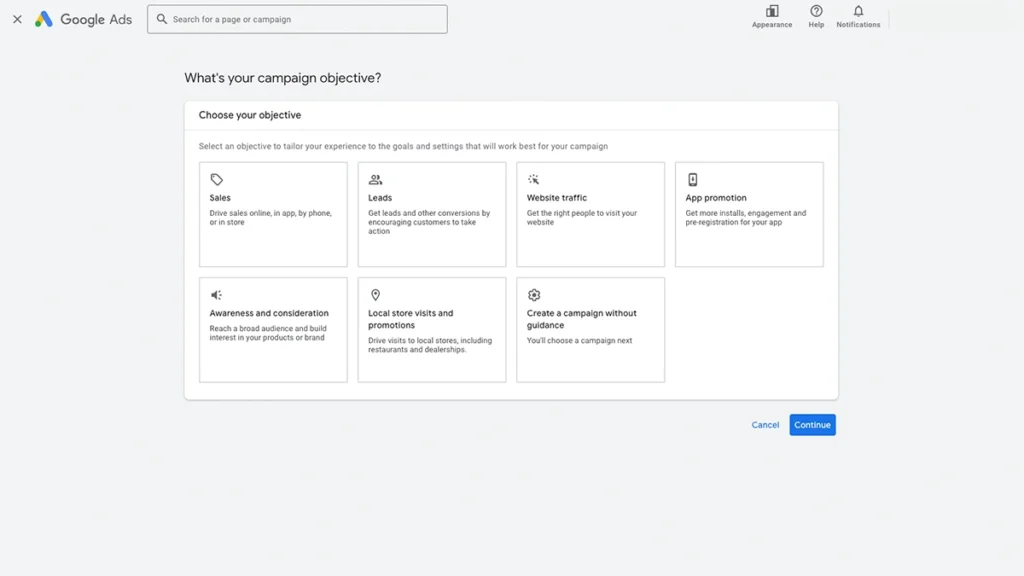
Google gives you several options here:
- Sales:
Best for e-commerce or direct sales - Leads:
For contact forms, bookings, or calls - Website traffic:
Great for driving visitors to your site (Recommended for most small businesses) - Product and brand consideration:
Used for video or display ads - Brand awareness and reach:
Ideal for brand-building campaigns - App promotion:
For mobile apps - Local store visits and promotions:
For businesses with physical locations - Create a campaign without a goal’s guidance:
For more advanced users
Our recommendation: Choose Website Traffic to start. It’s flexible and fits most service-based businesses.
Set Your Conversion Goal
Based on your selected objective, Google will ask you to pick a conversion goal. For website traffic, you’ll likely be given the option to track leads (e.g. a form submission or booking).
At this stage, just select “Submit lead form” or similar. We’ll show you how to set up conversion tracking properly later in the post.
select a Campaign Type
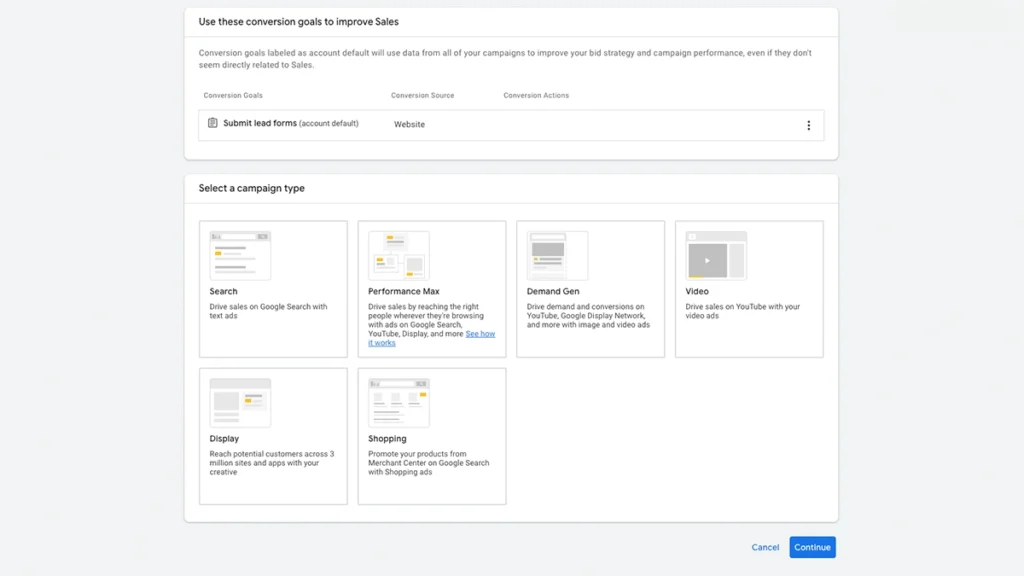
Now you’ll pick how you want your ads to be delivered. Here’s a quick overview of your options:
- Search:
Text ads shown on Google Search results (Recommended for beginners) - Performance Max:
Multi-channel ads across Search, Display, YouTube, Gmail, and Maps - Display:
Visual ads on websites and apps - Video:
YouTube ads - Shopping:
For e-commerce with product feeds - Demand Gen:
For video and visual campaigns across YouTube, Discover, and Gmail
Beginner Tip: Choose Search.
Enter Your Website URL & Name Your Campaign
You’ll be asked to enter the URL of the page you want to send traffic to. This should be a dedicated landing page — not just your homepage — that matches your campaign goal.
Then, give your campaign a clear name so you can track it later (e.g. “Web Traffic – July 2025 – Local Leads”).
7. Bidding Strategy
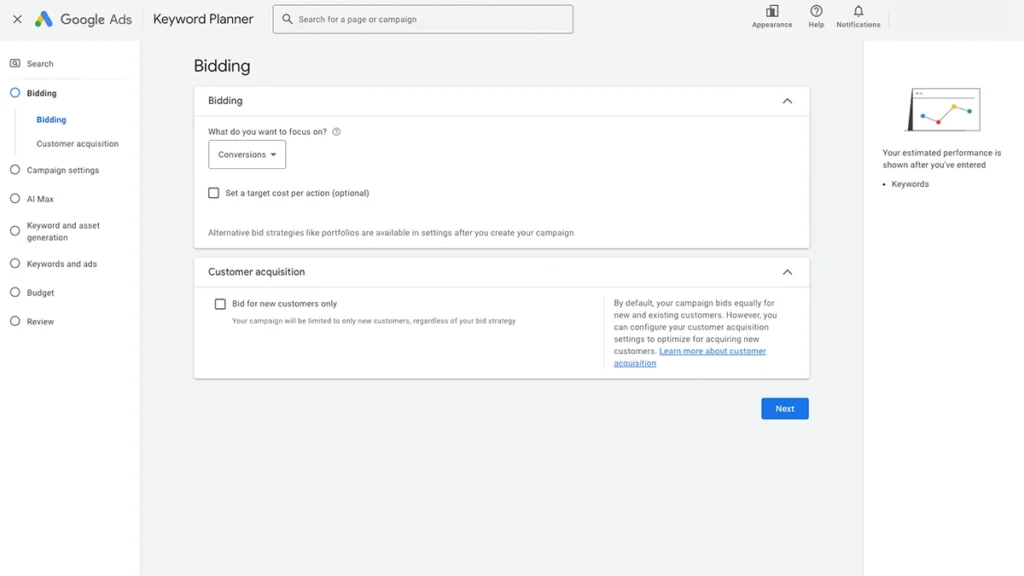
Google will ask how you’d like to measure success.
- Focus on Conversions:
Recommended if you’ve set up conversion tracking - Focus on Conversion Value:
If you want to maximise revenue or value per sale - Maximise Clicks:
If you don’t have conversion tracking set up yet
You can also set a Target CPA (cost per action) or Target ROAS (return on ad spend) if you want Google to optimise around your ideal numbers. When you are just starting out, it is easier to leave these settings alone.
Start Simple: Choose Focus on Conversions. You can always refine later.
8. Campaign Settings
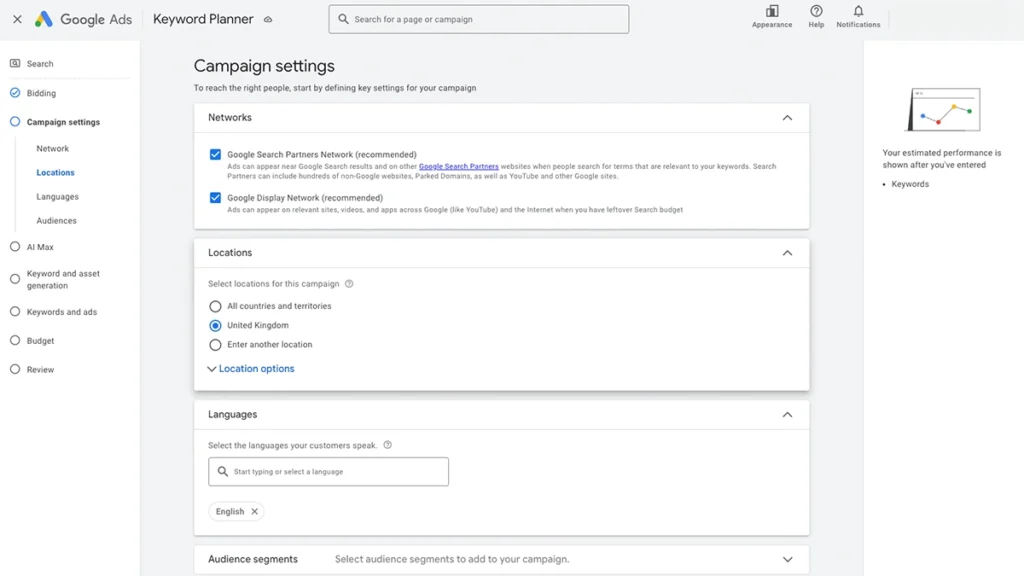
Next, you’ll configure a few important details:
Networks:
By default, Google will tick:
- Search Network (recommended)
- Display Network (untick this to start – it can waste budget)
Only keep Search Network selected for now.
Location targeting:
Choose where you want your ads to appear:
- Countrywide
- Specific cities or regions
- A radius around your business
Pro tip: Use location targeting to focus on areas where you actually offer services — this helps avoid wasting clicks.
Language:
Set the language your audience speaks — usually English for UK businesses.
More Settings:
- Ad schedule – Show ads during business hours only
- Campaign URL options – For tracking templates (advanced)
- Start and end dates – Set campaign length if needed
9. AI Max for Search campaigns
AI Max is Google’s push to bring the power of automation to traditional Search campaigns — giving them some of the smart, machine-learning-driven optimisation typically seen in Performance Max campaigns, but within a Search-only setup.
When enabled, AI Max uses Google’s algorithms to:
- Automatically choose keyword match types
- Adjust bids in real-time to maximise conversions
- Optimise ad delivery based on user behaviour and intent
- Generate dynamic ad headlines and descriptions based on your landing page
Essentially, it blends traditional keyword targeting with smart automation, aiming to improve performance without needing constant manual input.
Our recommendation is to keep this toggled off – giving you complete control over your ads and their performance.
10. Keyword and asset generation
Let Google help you with a starting point for your keywords and ad assets.
Enter the dedicated landing page url of your website (not just your home page). Tell Google a little bit about your products or services.
Use keyword and asset generation as a starting point — not a final draft.
Review every suggestion carefully, refine the messaging to match your brand, and remove any keywords that don’t make sense for your business.
11. Time to Create Your Ads
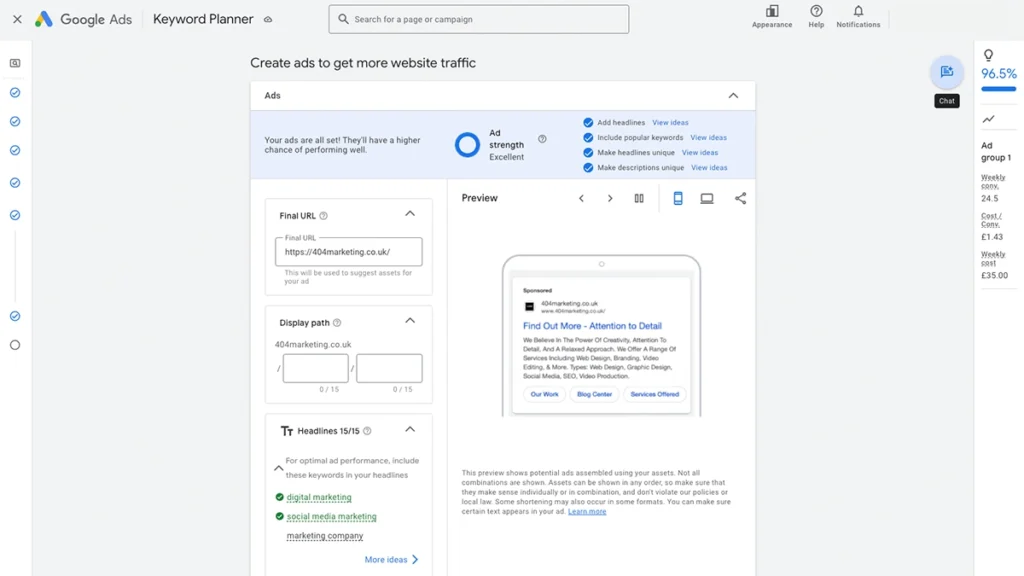
This is the most important step of the process – putting together the final ads that and selecting the target keywords that it will be shown for.
Start by entering any of the relevant keywords or phrases that you want you your ads to be shown for. These should be relevant to your products or services. Don’t worry, because the keywords that you select here are not final. You will be able to ad and remove keywords once your ad is live.
You’ll be prompted to write:
- Headlines (up to 15)
- Descriptions (up to 4)
- Final URL – the landing page
- Display Path – the link people will see in your ad
Best Practices:
- Include your main keyword in the headline
- Highlight benefits or USPs (e.g. 24/7 service, free quotes)
- Add a clear call to action like “Book Online” or “Call Now”
Google will rotate your headlines and descriptions to find the best-performing combinations.
12. Set Your Budget
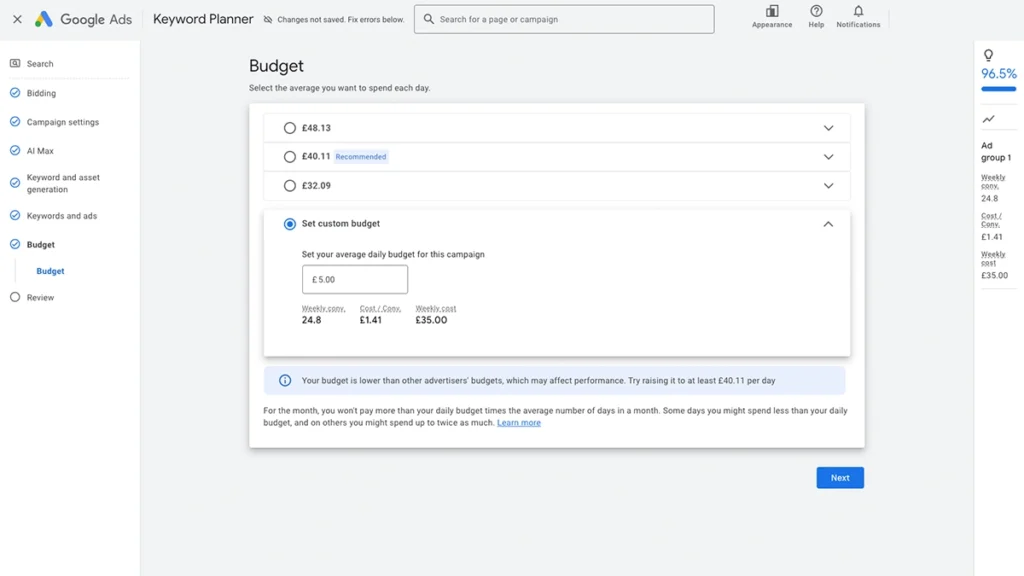
Google will give you a couple per determined budgets, as well as a recommended budget. Each option will include the expected average cost and number of conversions.
It is always could to take theses expected averages with a pinch of salt – the actual performance is usually lower.
Our suggestions is to start small—around £5 to £10 per day—and adjust as you learn what works.
Need help with setting up your Google Ads?
Get in touch
Tips to Make Your Ads More Effective
Setting up your campaign is just the beginning. Here’s how to get the most out of it:
- Create Dedicated Landing Pages:
Send visitors to a page that’s directly related to your ad, rather than your homepage. This improves your Quality Score and conversion rate. - Use Negative Keywords:
Negative keywords stop your ad from showing up in irrelevant searches. For example, if you sell luxury watches, you might want to exclude “cheap” or “free”. - Test Different Ads:
Run a few variations of your ad copy to see what performs best. Over time, you’ll learn what messaging resonates with your audience. - Track Conversions:
Set up conversion tracking so you know which ads are leading to sales, phone calls, or form submissions. This is essential for knowing your return on ad spend.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced advertisers make errors. Here are a few beginner pitfalls to steer clear of:
- Not defining a clear goal:
Know what success looks like before you start. - Ignoring mobile users:
Most searches happen on mobile. Make sure your site is mobile-friendly. - Setting and forgetting:
Monitor your campaigns regularly and adjust based on performance. - Using vague keywords:
Be as specific as possible to attract the right audience. - Skipping the research:
Take time to understand your audience and their search behaviour.
How to Set Up Conversion Tracking in Google Ads
If you’re spending money on ads, you need to know what’s delivering results. That’s where conversion tracking comes in.
A conversion is any valuable action a visitor takes on your website—like submitting a contact form, calling your business, making a purchase, or signing up to a newsletter. Google Ads allows you to track these actions so you can measure ROI and make smarter decisions.
1. create a conversion
In your Google Ads dashboard, select the plus button, and then conversion action.
Similar to how you would have set up a new campaign.
2. Choose Your Conversion Action
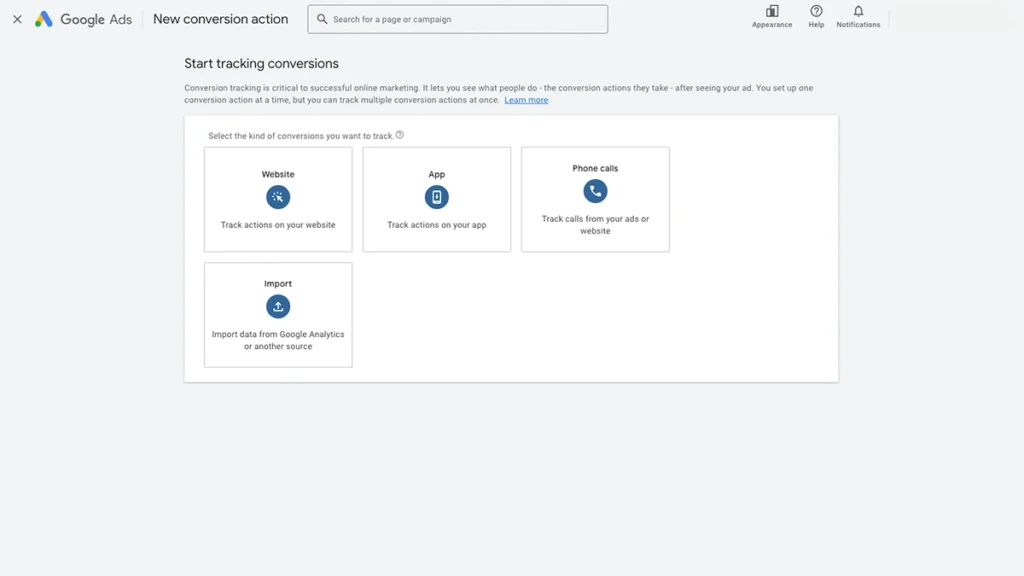
Decide what counts as a conversion for your business. This could be:
- A form submission
- A phone call from your website
- An online purchase
- A button click (like “Book Now”)
Beginner Tip: Start with Website as a conversion action. Especially if you have followed our guide for setting up a Search campaign to drive traffic to your website.
2. Create a New Conversion Action
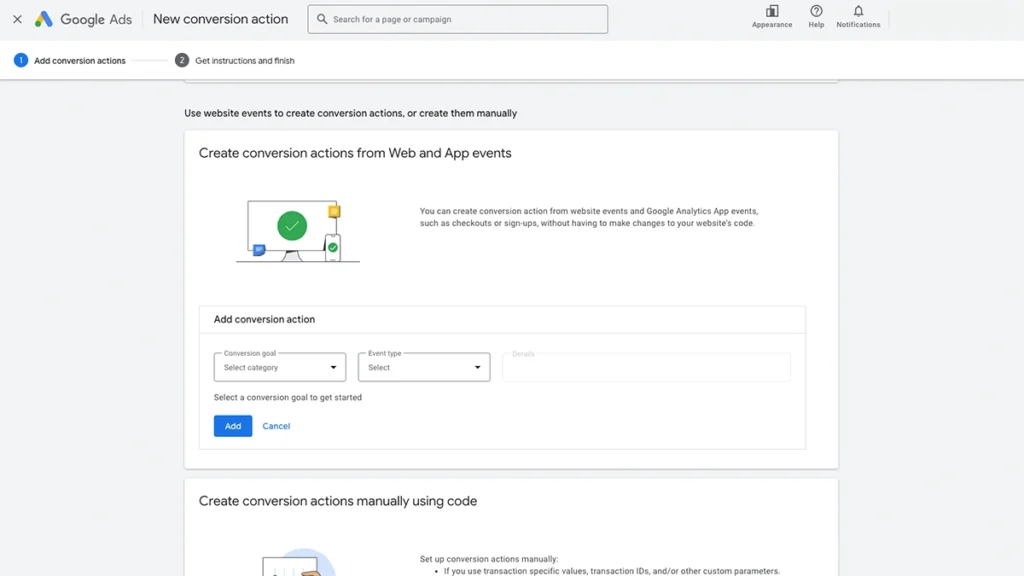
In this section it is best to create a conversion action using the promts, rather than creating a manual conversion action using code.
Our recommendation for beginners it to set it up like this:
- Conversion Goal: Submit lead form
- Event Type: Form submission
- URL: base URL of your website (that way it tracks conversion across your whole website)
You can also enter the URL of a specific page, if you want to track a specific form submission.
4. Install the Tracking Code
After setting up the conversion, Google will give you a tracking tag (or “global site tag”) and an event snippet.
You have two options:
- Manually install the code on your website (often in the
<head>section and on the “thank you” page) - Use Google Tag Manager, which makes it easier to manage tracking tags without touching code
If you use WordPress, plugins like Site Kit or Header & Footer Scripts can help insert the code.
5. Test Your Setup
After the tag is installed, test the conversion action by performing the desired activity (like submitting a form) and checking that Google Ads registers it.
Final Thoughts: Is Google Ads Right for Your Business?
Google Ads isn’t a silver bullet, but for small businesses and startups, it offers a fast, measurable way to generate leads and sales. If you’ve got a clear goal, a well-structured website, and the time to monitor your campaigns, it can be a powerful part of your marketing mix.
And if you’d rather not go it alone? That’s where we come in. At 404 Marketing, we help small businesses get the most out of their Google Ads campaigns—without blowing the budget.
Ready to Get Started?
If this Google Ads beginner’s guide for small businesses has helped you feel more confident, why not give it a try? Start with a small budget, test things out, and learn as you go.
Or, if you’d prefer a helping hand, get in touch with us—we’d be happy to chat.